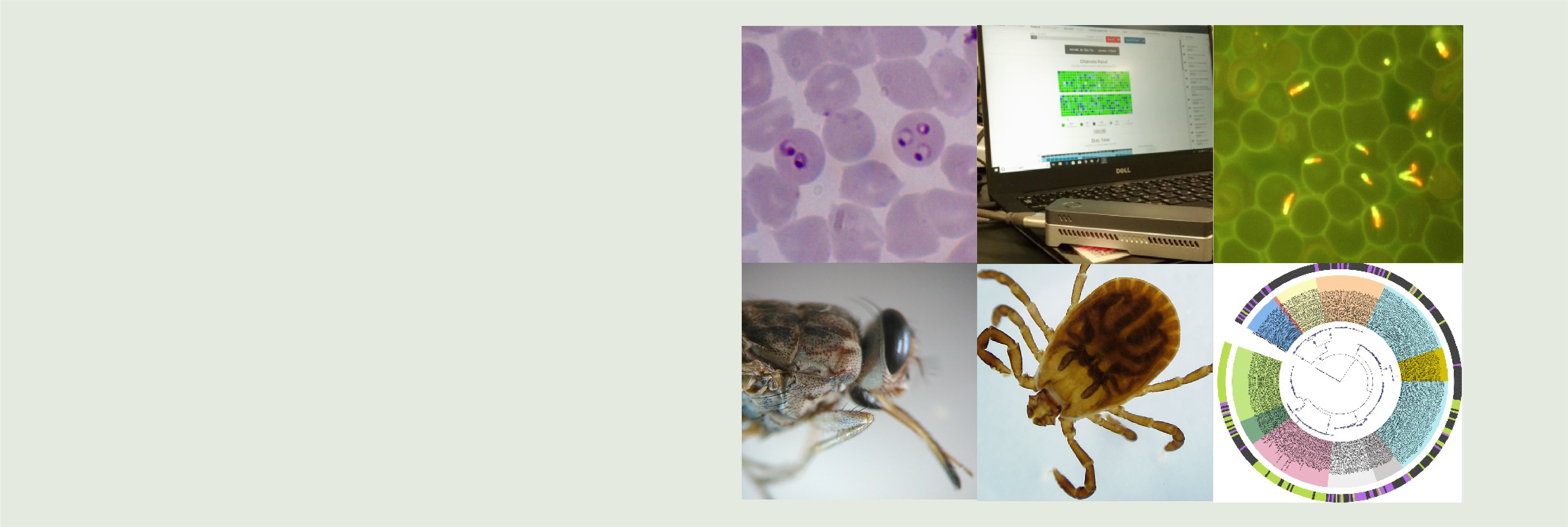
About us
We promote innovative parasitic disease research using molecular biological & genomic approaches. Our research interests include genomic analysis of protozoan diseases such as toxoplasmosis, trypanosomiasis, babesiosis, and leishmaniasis, single cell level transcriptome analysis, development of novel diagnostic methods, and protozoan-host-vector arthropod interactions. We actively collaborate with overseas research institutions in Zambia, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and other countries to implement innovative technologies in society based on fieldwork.

Explore Parasitology
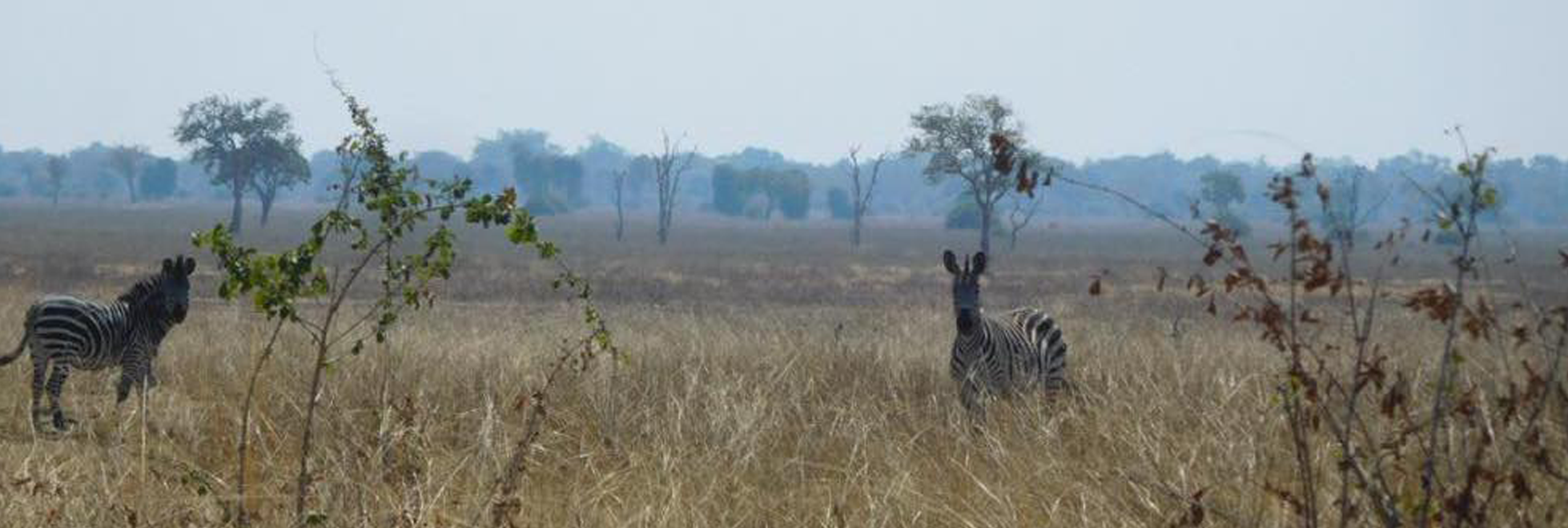
Parasites have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to subvert/evade host immune responses, and causing diseases in humans and animals. Understanding the diverse relationships between host cells and parasites, or between parasites and their arthropod vectors, is crucial for controlling these diseases.

mNGS for comprehensive pathogen detection
mNGS, or Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing, is a method that detects pathogen DNA or RNA by comprehensively analyzing the nucleic acids present in a sample. Theoretically, this single method can diagnose all pathogens. It is expected to become a standard infectious disease diagnostic method in the future because it can identify pathogens causing previously unexplained fevers and even new, emerging pathogens.
Through our research network in Thailand, Vietnam, and Bangladesh, we aim to conduct validation studies and implement mNGS as a new diagnostic method for infectious diseases.

One-Health control of Neglected Tropical Diseases
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are a group of illnesses that disproportionately affect impoverished communities, and have been largely overlooked, impairing human health and well-being. In a collaborative effort between Japan, Zambia, and Malawi, our project will focus on three particularly deadly zoonotic parasitic diseases: Leishmaniasis, African trypanosomiasis, and Echinococcosis. Our work will include epidemiological surveys, the development of diagnostic methods, and the practical application of a One-Health control approach.